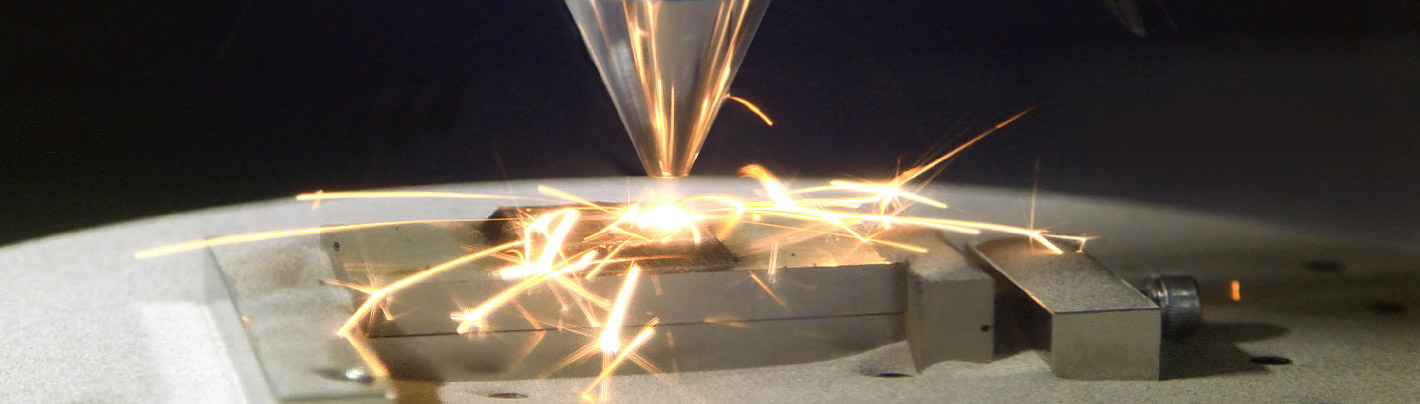
Gases we use
The PBF process commonly use nitrogen withmaterials like stainless steel, or Argon for othertypes of materials. We can help you analyse whatis the best performing mixture for your DED orPBF process. Another gas solution is helium, which is used in the EBM process, although beingexpensive for this process, it consumes a littleamount.
On the other hand, the FDM process uses argonnitrogen and small percentages of hydrogen inargon, but only in the metal sintering phase. Forfurther information don’t hesitate to contact us.
On the other hand, the FDM process uses argonnitrogen and small percentages of hydrogen inargon, but only in the metal sintering phase. Forfurther information don’t hesitate to contact us.
Argon for additive manufacturing
Thanks to its chemical-physical characteristics, Argon is a frequently used gas in the additive manufacturing processes. It's mostly used for those materials that are particularly reactive with oxygen or other air components.
Nitrogen fo Additive manufacturing
Under normal conditions nitrogen is an inert gas but which at high temperatures can react with some materials also used in 3D printing. The use of nitrogen in this process is indicated for austenitic steel powders.
Helium for Additive manufacturing
Helium is an absolutely inert and very light gas. Its chemical and physical characteristics make it ideal for both PBF and DED 3D printing processes, but it is very rare and expensive, so it is mainly used in EBM processes given the low gas consumption that this process has. In DED processes it is often used mixed with other gases.
Sanarc H for Additive manufacturing
Do you still have questions?
At Nippon Gases we are called “The Gas Professionals” for a reason, and it’s because we’ll be able to solve any doubt.