Competence onlaser process
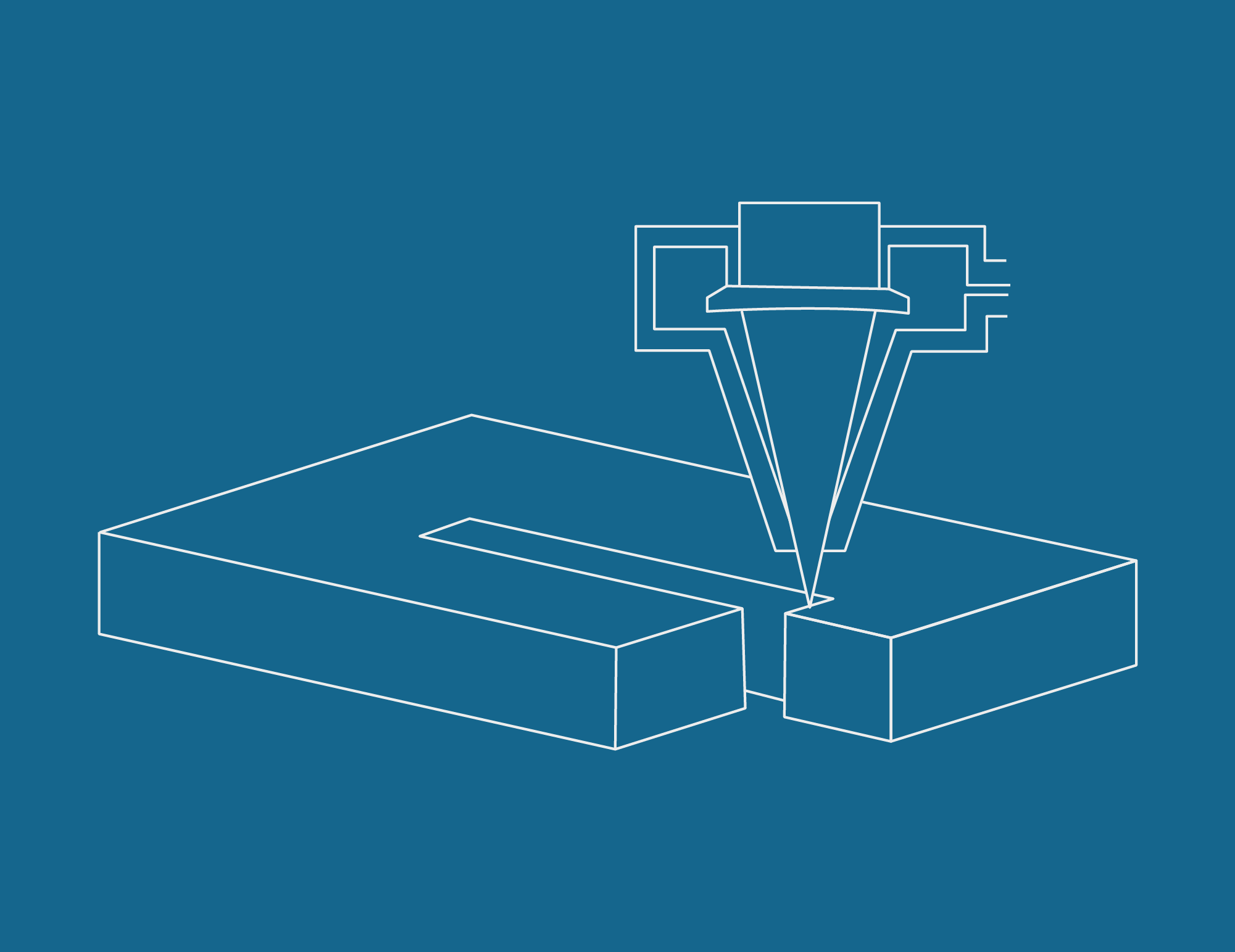
Cutting and welding sheet metal through the laser process requires gases and mixtures of high purity and production precision. Nippon Gases, through decades of experience in the production of gas,and in collaboration with the best manufacturers of laser systems, has developed production techniques capable of meeting the strictest requirements of manufacturers and beyond.
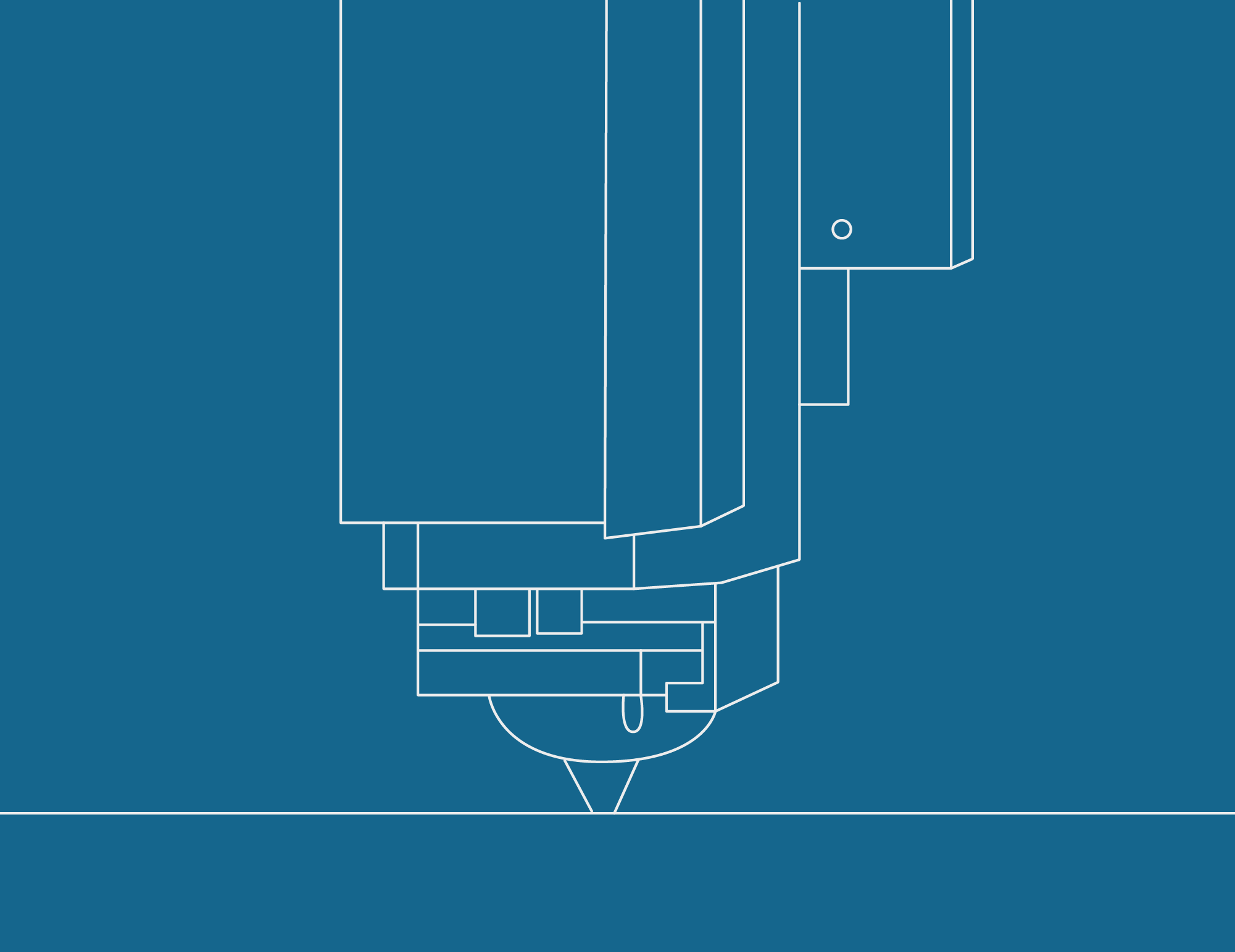
CO2 has a responsibility to create light emission for the effect of energy excitation, which becomes a laser beam after polarisation.
The job of this gas is double, into the source accumulate electron to move to CO2 when It needs to maintain excitation itself, in second as protection of metal sheet during the cutting process.
CO2 has a responsibility to create light emission for the effect of energy excitation, which becomes a laser beam after polarisation.
The job of this gas is double, into the source accumulate electron to move to CO2 when It needs to maintain excitation itself, in second as protection of metal sheet during the cutting process.
Metal reactivity
Every single material requires a
specific root protection gas.
Carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, titanium and
many others have metallurgical different characteristics
and a reactivity towards air.
During the laser cutting or welding phases it is essential
to protect or bring heat to allow the process, while the
absence of pollutants allows to exploit all the power of
the laser sources, whether CO2 or fiber.
CO2 has a responsibility to create light emission for the effect of energy excitation, which becomes a laser beam after polarisation.
The job of this gas is double, into the source accumulate electron to move to CO2 when It needs to maintain excitation itself, in second as protection of metal sheet during the cutting process.
Testing

